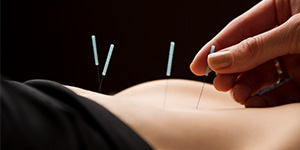
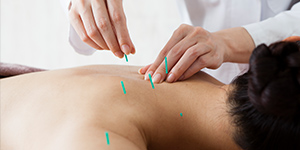
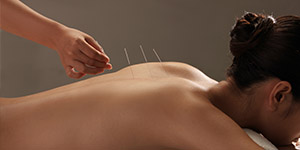
Gua Sha (brief introduction)
Gua Sha is a novel (to the West), unique, important and an effective remedy for pain, inflammation, immune support and improvement of skin health and appearance.
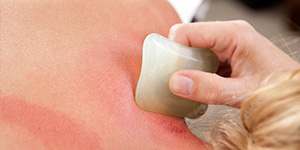
Gua Sha is a Traditional East Asian Medicine, TEAM healing technique that applies instrument-assisteduni directional (one-way) press-stroking of a lubricated area of body surface inorder to intentionally create transitory therapeutic petechiae (red spots on the skin, less than 2 mm in diameter).
Petechiae represent extravasation of blood underneath the skin (cutis) and indicates an increase in micro perfusion in skin surface.
Guameans 'to rub' or 'press-stroke'.
* Gua is applied in repeated even strokes onto skin’s surface.
Sha is a term that describes blood congestion in a tissue.
* blood congestionpatient may experience asstiffness, numbness, tinglingand'pain
Sha is also a term for small red or purple spotscalled petechiae.
* petechiaeare raised on the skin’s surfaceby applying GuaSha.
* suchpetechiae are therapeutic, transitory, and totally fade in 2-8 days depending on the strength of patient’s blood circulation.
Press stroking (gua) results in blood extravasation (sha) within the capillary net (without damage to the capillaries themselves), thereforesha is always red in colour, but can also be brown, blue, very deep red or nearly black, depending on the severity of the disorder.
The appearance, thecolour of Shaand its rate of fading can convey important information about the condition of the disorder.
* for example, if the shasurfaces quickly — the problem is more recent; if shais hard to raise to the surface — it can indicate that the problem lies deeper and is more long-standing, pale red sha— can be a symptom of blood deficiency, etc.
Today, tagged as “folk medicine”, GuaSha practice owes its recognition and existence among scientific scruples of the West to Arya Nielsen¹, PhD who has carried out the most extensive and systematic research on Gua Sha and has become Western authority of this traditional healing technique.
The highlights of her findings are summarised further on this page.
Effects of Gua Sha
Gua Sha moves chronic and acute stasis that is associated with such symptoms as stiffness, tingling, numbness and/or pain.
Gua Sha breaks the cycle of stasis that acupuncture alone sometimes cannot address.
In the body, stasis of Vital Substances:Qi, Blood, and Body Fluids, as well as dampness and phlegm can be caused by exterior, interior as well as other pathogenic factors(see section causes of pain).
Gua Sha immediately reduces pain local to anddistal to the treated area.
Pain relief lasts even after the sha (petechia) has completely faded.
Gua Sha may fully or partially resolve a presenting problem; it almost always helps.
Indications for Gua Sha
Being an excellent adjuvant, Gua Sha can be used alongside any other alternative medicine therapy methods as well as conventional medicine treatments, for example, physical therapy and medication.
Guasha was historically used to treat choleraand cholera-like disorders (So 1987) and is similar to the technique of frictioning used in early Western medicine to treat cholera (Jackson 1806).
Importance of Guasha also lies in its historical use in fevers which were associated with serious life-threatening illnesses.
Gua Sha is highly effective in the treatment of pain,stiffness and numbness and for functional disorders with impaired movement.
It resolves spasms and promotes normal circulation to the muscles, tissues, and organs directly beneath the area that is treated.
It is used for prevention and treatment of acute infectious illness, upper respiratory and digestive problems, and many other acute and chronic disorders.
In Chinese-language medical databasethere are case series for headache, migraine, facial paralysis, fever, influenza, adult and paediatric respiratory infection, sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and asthma - both for acute episodes and for prevention - and for paediatric enuresis.
Gua Sha is described in cases series of breast disease, mastitis, and hyperplasia, as well as for dysmenorrhea and recovery from induced abortion.
Gua Sha is applied in cases of acute and chronic hepatitis, for hypertension, insomnia, neurasthenia, skin problems, such as eczema, chloasma, shingles and post herpetic neuralgia, and eye problems, including styeand trachoma
Gua Sha is also described for postsurgical adhesions with intestinal obstruction.
Finally, Gua Sha has a special role in acute situations of thermal dysregulation that resonate with its therapeutic role in fever.
Gua Sha is especially effective for heat stroke, sunstroke, and also for patients who are cold or have an aversion to cold.
The healing mechanism of Gua Sha
The primary mechanism that lies behind the healing process of Gua Shais associated with connective tissue (to be more precise connective tissue proper, further mentioned just asconnective tissue) and involves following aspects:
Activation of connective tissue by unidirectional press stroking and creation of therapeutic petechiae
400% increase in microcirculation in surface tissue that endure days after the treatment,
Stimulation of immune and anti-inflammatory responses,
Therapeutic effect of nitric oxide (NO) release in the tissues,
Anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion,
* Cytokine fr. Greek cyto "cell" + kinisi "movement" small proteins that are important in cell signaling,
* Cytokines are released by cells and affect the behavior of other cells,
Upregulation of gene expression for an enzymeheme oxygenase-1 (HO-1),that has anti-oxidant, cytoprotectant, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Connective tissue is one of the largest and most extensive body organs.
It is a moist and fibrous membrane that is found in between other tissues (e.g. blood, lymph tissue, supportive tissue like cartilage and bone) everywhere in the body, including the central nervous system.
There is not a cell or space in the body that connective tissue does not integrate.
* It binds tissues into their organ shape, supplies tissues with vessels and ducts, properly fastens the organs within the body cavity, as well as binds organs to each other.
If all other tissue were removed, connective tissue would sustain the structure of the human form
Electrical andcellularsignalling of the connective tissueis responsive to mechanical forces (such as, Gua Sha, acupuncture, acupressure, cupping and massage) as such being the mediator of therapeutic effect.
Some connective tissueforms fascia(from Latin "band").
Fascia are tough sheets or bands beneath the skin, called subcutaneous fascia.
Subcutaneous fascia is spread throughout the bodyin a three-dimensional web, from head to feet, without interruption in two layers, as superficial fascia and deep fascia that adhere to each other.
Subcutaneous fascia serves as a 'body-wide signaling network'that transmits mechanical signals to and from the abundant fibroblasts, immune, vascular, endocrineand neural cells present within tissues, thus becoming an integral part of our Body’s Communication System (which comprises, nervousand endocrine systems, as well ascellular signaling (autocrine and paracrine).
Subcutaneous fascia aggregation sites coincide with the location of the acupuncture points.
Subcutaneous fascia as a 'body-wide mechanosensitive signalling network' researched by scientists today was understood by TEAM for over 2000 years in a medical paradigm based on ordinary human sensory awareness and interaction with the body, environment, health and illness.
For example, when outside Cold conditions are greater than a body's warming ability, Cold penetrates the membrane (subcutaneous fascia), thus stagnating Qi, Blood andBody Fluids.
This stagnation can communicate a deeper stagnation (in deep fascia) which in turn can damage the Internal Organs.
Unique characteristics of Gua Sha
Different manual therapies, vary in terms of intention, pressure, term of application, repetition, dosage, observable feedback, etc.
When it comes to Gua Sha there are at least three characteristics that distinguish this technique from other manual therapies:
1) Closely repeated, unidirectionalstroking that intentionally presses into the fascia,
2) Application is predominantly along a muscleand specifically not oscillating or across muscle tissue,
3) The intentional creation of transitory petechiaeandecchymosis(as a result of the first two techniques) Nielsen (2012).
This unidirectional fascial release activates anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion.
* Pressure and shear that create uni-axial fibroblast strain can account for improved range of motion (ROM), decreased edema, reduced analgesic requirements and 'long-term benefits despite short-term treatment'Standley and Meltzer (2008).
Four-fold increase in microcirculation
Modern research demonstrates that the therapeutic effect ofGua Shais achieved by radical (400%) increase in microcirculation of surface tissue that stimulates immune and anti-inflammatory responses that persist after treatmentNielsen et al. (2007).
* For example, massage has been shown to increase microperfusion slightly while engaged, but is not sustained when massage is stopped.
Stimulation of immune and anti-inflammatory responses
Gua Sha immediately induces a pain-relieving process local to anddistal to the treated area.
One theory of this effect is the release of nitric oxide (NO), as part of the process of increased perfusionand vasodilation.
Namely, in terms of its role in pain modulation: Endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase (ecNOS) mRNA expression has been shown to be time- and mechanical force dependent Ziegler et al. 1998b.
NO is a signalling molecule of gasthat is produced by many cells in the body, and is an important mediator in both health and disease.
For example NO is produced in the inner layer of the arteries called endothelium where it promotes relaxation of the artery wall, thus increasing blood flow and regulating blood pressure.
In the lungs it promotes relaxation of the bronchi and increased air flow
In the digestive system no promotes peristalsis, or a rhythmic motion that leads to complete digestion of food and healthy elimination.
* In preclinical studies NO was shown to help maintain gastric mucosal integrity, to inhibit leukocyte adherence to the endothelium, and to repair non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced damage, thus having a protective effect on the gastrointestinal tract (Lanas 2008).
NO was discovered in the early 1980 and was first recognised as a factor of a relaxation of the blood vessels “endothelium relaxation factor”.
The science of NOis extremely well documented.
there are over 112000 articles on Pubmed documented the effects of NO in bilogy.
NO was proclaimed as “Molecule of the Year” in 1992
This is an annual award made by AAAS journal Science for the most significant development in scientific research.
Research into the function of NO led, in 1998, to the Nobel Prize for discovery of the role of the nitric oxide as a cardiovascular signalling molecule.
Precursors of NO (as nitrates NO3 and nitrites NO2) are found in plant sources, especially in green leafy vegetables and are converted by human digestive system into NO by the chemical process called reduction.
The body’s ability to production of NO decreases with age.
NO release:
* Contributes to vessel homeostasisby inhibiting smooth muscle contraction, thrombocyte aggregation, and white cells adhesion to the interior walls of blood vessel (endothelium),
* dInitiatessmooth muscle relaxation →,
* dMediates vasodilation(widening of blood vessels) thus increasing blood flow due to a decrease in vascular resistance,
* dIs generated by phagocytes as a part of human immune response →,
* dHave effectson platelet(thrombocyte) function andinflammation,
* dProduces substantial pain relief by increasing circulation, decreasing nerve irritation, and decreasing inflammation (Hancock and Riegger-Krugh 2008).
Anti-oxidant, cytoprotectant, and anti-inflammatory effects
The sha that emerges as petechiae then immediately changes to ecchymosis (bruising-like appearance) and then begins to fade.
As sha fades, it becomes lighter, perhaps a bit brown, and finally the surface may appear yellowish before sha hyperpigmentation disappears.
These changes are due to the movement and removal of the extravasated blood, and the effect of the breakdown of hemoglobin , which in turn upregulates HO-1, CO, biliverdin and bilirubin that are anti-inflammatoryand cytoprotective.
A Harvard study showed that Guasha upregulates gene expression for an enzyme that is an anti-oxidant and cytoprotectant, HO-1 (heme oxygenase) 1, at multiple internal organ sites immediately after treatment and over a period of days following Gua Sha treatment Kwong et al. 2009.
Kwong's group providethe first study to show an immediate and sustained immune response from a traditional East Asian modality that has direct relevance to the treatment of internal organ and inflammatory problems.
HO-1 and its catalysates(biliverdin, bilirubin and carbon monoxide (CO)) exhibit not only anti-oxidative but also anti-inflammatory effects (Xia et al. 2008).
* For example, augmentation of HO-1expression attenuates allergic inflammation: HO-1 plays a protective role in allergic disease in part by inhibiting Th2 cell specific chemokines(Xia et al. 2008).
HO-1 regulates cell cycle and anti-smooth muscle hyperplasiaproviding protection in many disease models, such as asthma, organ transplant rejection, inflammatory bowel disease and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, even though the immune pathological mechanisms of these diseases are dissimilar Xia et al. 2008.
The physiology of HO-1 may also explain Guasha'santi-inflammatory effect in other responsive clinical conditions, such as fever, cough, asthma, bronchitis, emphysema, mastitis (Chiu et al. 2010), gastritis, musculoskeletal conditions such as neck pain (Braun et al. 2011), migraine (Schwickert et al. 2007), postherpetic neuralgia (Nielsen 2005), and so on.
Upregulation of the enzyme HO-1has been reported to be effective in the control of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and offers hepatoprotection in animal models Farombi and Surh 2006; Immenschuh et al. 2010; Protzer et al. 2007; Wunder and Potter 2003.
Induction of HO-1 results in decreased hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication, as well as protection from oxidative damage, suggesting a potential role for HO-1 in antiviral therapy and therapeutic protection against hepatocellular injury in HCV infection Zhu et al. 2008.
Gua Sha is used to treat symptoms of acute and chronic hepatitis in China.
Chan et al. (2011) describe a case in a Western journal where a single GuaSha treatment in a patient with active chronic hepatitis reduced levels of liver enzymes alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), modulated T-helper(Th)l/Th2 balance and enhanced HO-1, which they suggest is responsible for the hepatoprotective effect.
In this case, and in general, GuaSha may be effective in transiently reducing the inflammatory injury to the liver when chronic hepatitis B moves into the immune active phase indicated by liver function test.
Gua Sha has also shown significant beneficial effects on exercise endurance, glucose reserve and serum enzyme in rats.
This correlates with provider reports of Guasha's benefit for athletic fatigue(Fang et al. 2008), chronic fatigue (Ruan 2008; Wang 2002) and stress(Liu 2009; Geng 2010).
After treatment
Gua Shaprovides immediate relief, comfort and warmth.
Patient is advised to keep the treated area protected from wind, cold and direct sun until the Sha fades.
After treatment patient is advised to keep the treated area protected from wind, cold and direct sunlight until the shafades.
Please, allow 3-10 days for disappearance of petechiae before considering sunbathing or planning to wear body revealing clothing.
Ppatients are also encouraged to drink plenty of water (for maintenance of increased micro perfusion) and eat moderately.
The frequency of the treatment depends on the severity of the disorder.
The petechiae should have completely disappeared before considering Gua Sha on the same site ( which is after 3- 10 days)
However, if the disorder lies in another site, then Gua Sha can be applied
The response to Gua Sha (and other TEAM treatments) always differ from individual to individual.
Usually, there is a quick relief of symptoms and recovery, including esthetical improvement of the skin * within one, two or three sessions
Gua Sha is safe and has no side effects
Patients are also encouraged to drink plenty of water, eat moderately and most importantly treat or eliminate “energy and substance leaking” causes:
Excessive coffee drinking:
As a diuretic taken daily, excessive coffee depletes the body of water-soluble nutrients including B vitamins and vitamin C, as well as minerals such as calcium and magnesium,
* This will exacerbate any painful condition as well as fatigue the patient, increasing the desire for more coffee.
* Because caffeine occupies adenosine receptor sites, and adenosine relaxes muscles so they may return to and maintain their resting length, consistent caffeine intake canlead to muscle strain, tears and contractions, causing and retarding healing of injuries
* Caffeine also contributes to hot flush disorder in menopausal women
* The diuretic activity severely depletes the Yin
Excessive: sweating, urination, exercise, work, sexual activity, menstrual bleeding,
Excessive alcohol consumption,
Illness,
Lack of sleep,
Recreational drugs like nicotine, pot, cocaine, amphetamines,
Distress (unresolved, ongoing stress),
Dmotional strain (from work or relationships).
Contraindications for Gua Sha
Gua Sha is not applied:
Directly to an area that has just been recently injuredand/or not healed.
Where there is bruising, abrasion, sunburn, rash or a break in the skin, pimples or moles.
On the abdomen of a pregnant woman.
To extremely deficient patients(weak, tired) (GuaSha should be applied with care).
* However, Gua Sha is indicated in most cases of Deficiency.
The site of the remaining sha from previous treatment.
* The petechiae should have completely disappeared before considering Gua Sha onthe same site, however if the disorder lies in another site , then Gua Sha can be applied.
Does Gua Sha hurt?
Gua Sha can be simplistically described as an invigorating, deep, intensive type of massage.
Patients have varying levels of tolerance.
* Some can sleep through Gua Sha; others find it uncomfortable in certain sites of the body, a few find Gua Sha - impossible.
* Levels of tolerance depend on general well being of the patient, that is, degree of tiredness, general tension of the body (stressed patients), bleeding cycle (in women), etc.
Footnote¹Arya Nielsen, PhD is a practitioner, teacher, author, and a researcher, who by using historical examinations of East Asian medical texts, cross cultural historical documents, contemporary scholarly sources, interviews with living elder practitioners and her own keen clinical experience brought Gua Sha to the Center of Oriental medicine.
Dr. Nielsen has a faculty appointment at a New York teaching hospital, Beth Israel Medical Centre, where she treats patients and also directs Acupuncture fellowship for Inpatient Care through the department of Integrative Medicine.
In anatomical terms a connective tissue properis one of the four types of biological tissue that supports, connects, or separates different types of tissues and organs in the body.
All connective tissue apart from blood and lymph consists of three main components:
* Fibers, (elastic and collagenous fibers), ground substance and cells.
Is characterized by the abundance of extracellular components (fibers and intercellular substances).
The other three types are epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue.
Connective tissue proper consists ofloose connective tissue and dense connective tissue (which is further subdivided into dense regular and dense irregular connective tissues.
A fybroblast is a type of cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, the structural framework (stroma) for all tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing.